
MRI - Longitudinally extensive transverse myelitis - T2 hypersignal on vertebral segments C2-C5, Th2-Th5 and Th7-Th11 |
Bilateral Motor Deficit of the Lower Limbs (Romania)
Clinical Area:
Infectious diseases
We report the case of a 15-year-old male teenager admitted in our clinic for bilateral motor deficit of the lower limbs associated with the impossibility to defecate within the last 48 hours and to urinate for approximately 10 hours. The symptoms developed progressively with severe fatigue within th ...
|
|

ECG - Complete congenital atrioventricular block |
Complete congenital atrioventricular block (Romania)
Clinical Area:
Cardiology
We report the case of a term male newborn, appropriate for gestational age, gestational age 39 weeks and 4 days, who was born in our 3rd level maternity. From the anamnesis, we noted that the pregnancy was monitored, with a prenatal diagnosis of complete congenital atrioventricular block. At admissi ...
|
|

Figure 1. The left ventricle from which the pulmonary artery originates; Figure 2. Large vessels with the Aorta located anteriorly and the pulmonary artery posteriorly |
D-Transposition of the Great Arteries (Romania)
Clinical Area:
Cardiology
We report the case of a term male newborn, appropriate for gestational age, gestational age 38 weeks, who was born in our 3rd level maternity. From the anamnesis, we noted that the pregnancy was monitored, with an prenatal diagnosis of complex congenital cardiac malformation: Transposition of great ...
|
|

First image - antero-posterior thoraco-abdominal x-ray; Second image - Latero-lateral thoraco-abdominal x-ray; Both images with intestinal aeration suddenly interrupted in the middle abdominal floor; opacity in the lower abdominal floor |
Early-onset neonatal sepsis associated with ileal atresia (Romania)
Clinical Area:
Infectious diseases
We report the case of a term newborn female, small for gestational age, born at a gestational age of 38 week and 3 days in our 3rd level maternity. The anamnesis pointed out that he originated from an unmonitored pregnancy. At admission, she presented grunting, oxygen saturations 80% in ambient air ...
|
|

Antero-posterior chest x-ray - a dark lucency around the edge of the left lung pleural line with a significant portion of the affected hemithorax without lung markings and mediastinal shift |
Neonatal pneumothorax secondary to respiratory distress syndrome (Romania)
Clinical Area:
Pulmonology
We report the case of a preterm newborn female, the second twin, with very low birth weight, born at 27 weeks of gestation in our 3rd level maternity. At admission, she presented functional respiratory syndrome represented by cyanosis, grunting and retractions. On auscultation, the breath sounds wer ...
|
|

Antero-posterior chest X-ray - low lung volumes, ground-glass reticulo-granular appearance with air bronchograms |
Neonatal pneumothorax secondary to respiratory distress syndrome (Romania)
Clinical Area:
Pulmonology
We report the case of a preterm male newborn, the second twin, with very low birth weight and a gestational age of 32 weeks who was born in a 1st level maternity and transferred to our 3rd level maternity at 10 hours after birth. At admission, he presented functional respiratory syndrome represented ...
|
|

Cranial ultrasound, coronal section – 3rd degree intraventricular hemorrhage, in the left ventricle; 2nd degree intraventricular hemorrhage without ventricular dilatation, in the right ventricle. |
Neonatal seizures secondary to grade III intraventricular hemorrhage (Romania)
Clinical Area:
Neurology
We report the case of a preterm female newborn, with very low birth weight and gestational age of 27 weeks of gestation which was born in our 3rd level maternity. We perfomed serial cranial ultrasounds. In the 1st day of life, there were no signs of intraventricular hemorrhage. On the 3rd day of lif ...
|
|

Cranial ultrasound, coronal section – Neonatal posthemorrhagic hydrocephalus secondary to intraventricular hemorrhage |
Neonatal posthemorrhagic hydrocephalus secondary to intraventricular hemorrhage (Romania)
Clinical Area:
Neurology
We report the case of a preterm male newborn, with extremely low birth weight and gestational age 25 weeks of gestation which was born in our 3rd level maternity. He was born by cesarean section performed for premature detachment of the normally inserted placenta. We performed serial cranial ultraso ...
|
|

Monitoring sheet prepared by the nurse |
Late-onset neonatal sepsis with septic shock (Romania)
Clinical Area:
Infectious diseases
We report the case of a preterm female newborn, the first twin, with extremely low birth weight born at 27 weeks of gestation in our 3rd level maternity. The anamnesis pointed out that the pregnancy was monitored, and the mother benefited from corticotherapy administered antepartum. At admission, th ...
|
|

Chest X-ray - Acute pulmonary edema |
Acute pulmonary edema (Romania)
Clinical Area:
Cardiology
Acute pulmonary edema is a frequently encountered medical emergency marked by severe shortness of breath, orthopnea, and pulmonary congestion due to left ventricular failure. For nurses, the rapid recognition of the clinical presentation (severe dyspnea with orthopnea, which prevents the patient fro ...
|
|

Electrocardiography - ventricular fibrillation |
Ventricular fibrillation (Romania)
Clinical Area:
Cardiology
Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) is necessary to save the life of a person without a pulse and breathing. After 4 minutes without oxygen, irreversible damage occurs to the brain. In such case is vital to initiate CRP. Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) is the only chance of survival in such situ ...
|
|

Electrocardiography - asystole |
Asystoly (Romania)
Clinical Area:
Cardiology
Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) is necessary to save the life of a person without a pulse and breathing. After 4 minutes without oxygen to the brain, irreversible damage occurs, making the timely application of this maneuver vital in such cases. Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) is the only ch ...
|
|

Patient with septic shock + advanced hemodynamic monitoring which suggest the state of sock |
Septic shock (Romania)
Clinical Area:
Infectious diseases
Sepsis is a life-threatening organ dysfunction caused by a dysregulated host response to infection. Sepsis is identified by an acute change in the Sequential Organ Failure Assessment (SOFA) score of 2 or more points, which reflects organ dysfunction or failure. The SOFA score evaluates the function ...
|
|

Meningoencephalitis in an 4 old month infant |
Meningoencephalitis (Romania)
Clinical Area:
Infectious diseases
Meningoencephalitis is a medical condition characterized by the inflammation and/or infection of meningeal membrane and brain at the same time. It’s life-threatening, and early treatment is essential. Commonly meningoencephalitis is caused by viral infections (herpes simplex virus, enteroviruses), ...
|
|

Right sylvian ischemic stroke on cranian computer tomography |
Stroke (Romania)
Clinical Area:
Neurology
Stroke, a medical emergency caused by interrupted blood flow to the brain, requires prompt recognition and intervention to minimize brain damage and improve outcomes. For nurses, early identification of stroke symptoms—such as sudden weakness, facial drooping, difficulty speaking, or confusion— ...
|
|

Pacient with hypoglycemic coma - Micro-Astrup |
Hypoglycemic coma (Romania)
Clinical Area:
Neurology
Hypoglycemic coma, a severe complication of low blood sugar levels, can be life-threatening if not addressed promptly. For nurses, recognizing early signs of hypoglycemia—such as confusion, sweating, weakness, or tremors—is critical to prevent progression to coma. In the event of a hypoglycemic ...
|
|

Arterial blood gas in a hyperglycemic crisis |
Diabetes- Hyperglycemic crisis (Romania)
Clinical Area:
Internal medicine
The occurrence of a hyperglycemic crisis, often associated with severe complications such as diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) or hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state (HHS), can lead to life-threatening conditions that significantly increase the risk of mortality, regardless of the patient’s age. Therefore, ...
|
|

Anaphylactic shock |
Anaphylactic shock (Romania)
Clinical Area:
Internal medicine
Anaphylactic shock, a severe and potentially life-threatening allergic reaction, can result in rapid deterioration and increased mortality, regardless of the patient’s age. Therefore, early diagnosis and prompt treatment are critical in preventing fatal complications and ensuring the best possible ...
|
|

Hemorrhagic shock – digestive bleeding in a 48-year-old man |
Hemorrhagic shock (Romania)
Clinical Area:
Internal medicine
Hemorrhagic shock from digestive bleeding is a serious and often life-threatening condition that can escalate quickly, putting patients of any age at risk. Rapid diagnosis and immediate treatment are essential to control the bleeding and stabilize the patient, improving their chances of recovery. Th ...
|
|

Pulmonary embolism |
Pulmonary embolism (Romania)
Clinical Area:
Internal medicine
Pulmonary embolism (PE) is a serious condition in which a blood clot obstructs the pulmonary arteries, potentially leading to life-threatening complications. Nurses play a critical role in the early detection and management of PE, as symptoms can often be subtle or resemble other conditions. Recogni ...
|
|

COPD - hypercapnic coma - Astrup examination |
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) - hypercapnic coma (Romania)
Clinical Area:
Pulmonology
Hypercapnic coma, a severe complication of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), occurs when high levels of carbon dioxide build up in the blood due to respiratory failure. For nurses, recognizing and managing this condition is critical, as it requires immediate intervention. Nurses must be ...
|
|

Pneumothorax |
Pneumothorax (Romania)
Clinical Area:
Pulmonology
Pneumothorax, the collapse of a lung due to the presence of air in the pleural space, is a potentially life-threatening condition that requires immediate attention. For nurses, early recognition of pneumothorax symptoms—such as sudden chest pain, shortness of breath, and decreased breath sounds on ...
|
|

Acute respiratory failure - in an asthma crisis |
Acute respiratory failure (Romania)
Clinical Area:
Pulmonology
Acute respiratory failure is a life-threatening condition where the lungs cannot provide sufficient oxygen to the blood or remove enough carbon dioxide. For nurses, recognising and responding quickly to signs such as shortness of breath, rapid breathing, confusion, or cyanosis is critical. Nurses ar ...
|
|

EEG epilepsy pattern |
Seizures (Romania)
Clinical Area:
Neurology
Convulsions, or seizures, are sudden, uncontrolled electrical disturbances in the brain that can cause changes in behavior, movement, or consciousness. For nurses, quick recognition and management of convulsions are crucial. Nurses must prioritize patient safety by ensuring a clear environment to pr ...
|
|

Monitor with vital signs |
MRSA-Associated Systemic Sepsis in Neonate (Greece)
Clinical Area:
Infectious diseases
You are caring for Baby J, a preterm infant born at 30 weeks gestation, now 12 days old, in the Neonatal Intensive Care Unit (NICU). Baby J has been receiving parenteral nutrition through a peripherally inserted central catheter (PICC) and small enteral feedings of expressed breast milk. Over the pa ...
|
|

Important findings on blood results and blood cultures |
Central Line Associated Bloodstream Infection (CLABSI) in NICU patient (Greece)
Clinical Area:
Infectious diseases
You are caring for a male preterm infant born at 28 weeks gestation, now 18 days old, in the Neonatal Intensive Care Unit (NICU). The infant has a peripherally inserted central catheter (PICC) placed three days ago, which is being used for total parenteral nutrition (TPN) and intermittent medication ...
|
|

Infant with abdominal distension on physical examination |
Suspected Necrotizing Enterocolitis (NEC) in a Neonate (Greece)
Clinical Area:
Infectious diseases
Baby A, a preterm infant born at 29 weeks gestation, is now 9 days old and has been under care in the Neonatal Intensive Care Unit (NICU). The infant had been stable and receiving expressed breast milk through enteral feeds for the past five days. However, during your shift, Baby A develops alarming ...
|
|
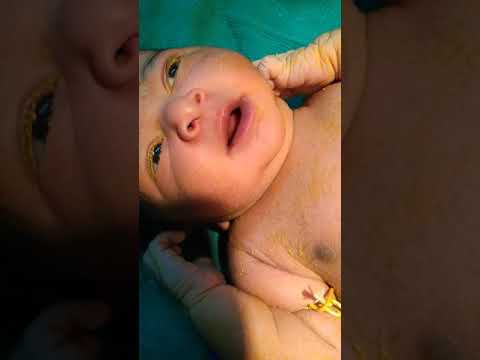
Video with Nasal Flaring in Newborn |
Neonate with suspected RSV (Greece)
Clinical Area:
Infectious diseases
A male infant was born to a 26-year-old mother with no significant medical history. The infant, delivered at 35 weeks gestation due to a premature rupture of the membranes with a birth weight of 2 kg, initially demonstrated a stable postnatal course and was discharged in good condition after four da ...
|
|

Chest X-ray showing patchy infiltration in both lungs and predominantly in the right lower lung |
Neonatal Ventilator-Associated Pneumonia (VAP) caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa (Greece)
Clinical Area:
Infectious diseases
You are caring for a 27-week preterm infant, now 15 days old, in the Neonatal Intensive Care Unit (NICU). The infant has been mechanically ventilated since birth due to severe respiratory distress syndrome (RDS), requiring continuous respiratory support. During your shift, you observe a marked and c ...
|
|

Pneumothorax |
Pneumothorax (Portugal)
Clinical Area:
Pulmonology
Pneumothorax in newborns is a condition in which air accumulates in the pleural space, between the lung and the chest wall, causing partial or complete collapse of the lung. This condition can be serious, especially in newborns, and requires immediate clinical attention.
Delivery at 36 weeks and 5 ...
|
|

Neonatal Asphyxia |
Perinatal Asphyxia (Portugal)
Clinical Area:
Neurology
Newborn female admitted shortly after birth to the Neonatology Unit due to fetal asphyxia. Delivered by emergent cesarean section under general anesthesia following a failed instrumented dystocic delivery (vacuum extraction followed by forceps), at 39 weeks of gestation. Apgar scores were 4, 6, and ...
|
|

Comparison of normal heart circulation and Tetralogy of Fallot |
Tetralogy of Fallot (Portugal)
Clinical Area:
Cardiology
Tetralogy of Fallot (TOF) is a congenital heart defect that consists of four abnormalities in the heart's structure. These defects affect blood flow and reduce the oxygen levels in the body. The four key components of TOF are:Pulmonary Stenosis – Narrowing of the pulmonary valve or artery, restric ...
|
|

Chest x-ray showing normal lung fields and slight cardiomegaly. |
Neonatal pulmonary atresia with an intact ventricular septum (Greece)
Clinical Area:
Cardiology
A 37-year-old, G1 P0 woman gives birth to a male neonate at 40 weeks of gestational age, with a birth weight of 3200 g. Past medical history was unremarkable, but the prenatal care throughout the pregnancy was suboptimal.
The infant was born by normal vaginal delivery. He cried immediately after b ...
|
|

Chest x-ray showing signs of pulmonary overcirculation and pulmonary edema |
Neonatal coarctation of the aorta (Greece)
Clinical Area:
Cardiology
A 36-year-old, G4 P3 woman gives birth to a male neonate at 41 weeks of gestational age, with a birth weight of 3450 g. Regarding her past medical history, she suffered from diabetes mellitus with poor control, and she had suboptimal prenatal care throughout her pregnancy.
The infant was born by n ...
|
|

Chest x-ray showing normal lung fields and cardiomegaly. |
Neonatal pulmonary atresia with cardiogenic shock due to severe aortic stenosis (Greece)
Clinical Area:
Cardiology
A 28-year-old, G2 P1 woman gives birth to a female neonate at 37 weeks of gestational age, with a birth weight of 2700 g. Past medical history was unremarkable. The mother had limited prenatal care throughout the pregnancy. There was no history of maternal medications and there was no family history ...
|
|

12-lead EKG showing narrow-complex supraventricular tachycardia. |
Neonatal supraventricular tachycardia (Greece)
Clinical Area:
Cardiology
A male newborn infant is brought to the NICU due to tachycardia. The infant was born at term by normal vaginal delivery to a 28-year-old G1P0 now 1 woman. He cried immediately after birth, with good respiratory effort, heart rate >100 b/m, good tone, and normal skin color. His Apgar scores were 8 in ...
|
|

Chest x-ray showing cardiomegaly |
Neonatal cardiac tamponade (Greece)
Clinical Area:
Cardiology
A female newborn was born at 31 weeks of gestational age, with a birth weight of 1350 g, by vaginal delivery due to preterm onset of labor, to a 33-year-old G4P3 woman. The mother had adequate prenatal care during pregnancy and an unremarkable past medical history. She received no medications and ha ...
|
|

Exchange Transfusion |
Exchange Transfusion in a Newborn (Portugal)
Clinical Area:
Internal medicine
Exchange transfusion is a clinical procedure used in newborns with severe jaundice caused by ABO blood group incompatibility between the mother and the baby. This condition most commonly arises when the mother has blood type O and the newborn has type A or B.
In such cases, maternal anti-A or anti- ...
|
|

Erb’ s Palsy/Brachial Plexus injury |
Erb-Duchenne paralysis in neoate (Greece)
Clinical Area:
Neurology
Delivery was by an emergency Caesarean section because of a labour and fetal distress at 38 weeks of gestation. The pregnancy was uneventful until the labour at 38 weeks. The mother was healthy and was diabetic. The birthweight was 3.8 kg. The presentation was cephalic. Examination of the birth reco ...
|
|

Brain MRI of a neonate with Neonatal HIE |
Neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy (HIE) (Greece)
Clinical Area:
Neurology
A term newborn was born at 38 weeks of gestational age, with a birth weight of 3500 g, delivered by caesarean section due to profound fetal bradycardia, to a 33-year-old woman. The mother had adequate prenatal care during pregnancy and an unremarkable past medical history.
The infant didn't cry im ...
|
|

Cranial Ultrasound imaging of preterm neonate reported as a case of Intraventricular haemorrhage. CUS grading of GMH/IVH; arrowheads point to GMH, arrows to the presence of clot in the ventricle cavity; asterisk is choroid plexus.. |
Intraventricular haemorrhage in a preterm infant (Greece)
Clinical Area:
Neurology
A 43-year-old primipara presented with severe hypertensive disorder of pregnancy and fetal growth restriction (FGR) at 19 gestational weeks. At 23 6/7 gestational weeks, an emergency cesarean section was conducted due to worsened hypertensive disorders of pregnancy (HDP) and a non-reassuring fetal s ...
|
|

Hypotonic neonate with Prader Willy Syndrome |
Hypotonia in a neonate (Greece)
Clinical Area:
Neurology
This patient is a full-term male infant and fourth child of non-consanguineous parents. He was conceived naturally, and his mother was well throughout the pregnancy. An amniocentesis performed at 17 weeks’ gestation showed normal chromosomes: 46,XY. Late-onset growth restriction occurred from 32 w ...
|
|

MRI - Brain magnetic resonance imaging of the neonate reported as case. Intracerebral hematoma at the right hemisphere of the brain on the border of the temporoparietal lobe and a second one in the left temporal lobe |
Intracerebral hematoma in term neonate (Greece)
Clinical Area:
Neurology
A female neonate of 38 weeks gestational age, weighing 3270 g, was born in good general condition, by vaginal delivery to a 28-year-old gravida 2 mother. The pregnancy was complicated by maternal diabetes. Apgar scores were 8 at first minute and then 9 and 10 at third and fifth minutes, respectively ...
|
|

A. Chest x-ray showing RDS. B. Ventilator waveforms and loops showing extubation. C. Ventilator waveforms showing a normal volume – time waveform. |
Neonatal ventilation management – self extubation (Greece)
Clinical Area:
Pulmonology
A male preterm neonate was born at 27 weeks of gestational age, with a birth weight of 1000 g, by vaginal delivery due to preterm onset of labor, to a 26-year-old G1P0 woman. The mother had inadequate prenatal care during pregnancy and an unremarkable past medical history. She received no medication ...
|
|

A. Ventilator pressure – volume loop showing decreased compliance. B. Cold light transillumination of the chest showing right sided pneumothorax. C. Chest x-ray showing neonatal RDS and a chest drain in the right side in situ. |
Neonatal ventilation management – neonate with pneumothorax (Greece)
Clinical Area:
Pulmonology
A male preterm neonate was born at 30 weeks of gestational age, with a birth weight of 1500 g, by vaginal delivery due to preterm onset of labor, to a 28-year-old G1P0 woman. The mother had inadequate prenatal care during pregnancy and an unremarkable past medical history. She received no medication ...
|
|

A. Ventilator pressure – volume loop showing decreased compliance. B. Cold light transillumination of the chest showing right sided pneumothorax. C. Chest x-ray showing neonatal RDS and a chest drain in the right side in situ. |
Neonatal ventilation management – neonate with bronchiolitis (Greece)
Clinical Area:
Pulmonology
A male ex-preterm neonate was readmitted to the neonatal unit at 44 weeks of post menstrual age due to fever and respiratory distress.
The neonate was born at 28 weeks of gestational age, with a birth weight of 990 g, by vaginal delivery due to preterm onset of labor, to a 28-year-old G1P0 woman. ...
|
|

A. Chest x-ray showing pleural effusion bilaterally. B. Chest x-ray showing chest drains in situ bilaterally. |
Neonatal respiratory – pleural effusion (Greece)
Clinical Area:
Pulmonology
A male infant was born at 30+6 weeks’ gestation with a birth weight of 1950 g. The patient was born by Cesarean section, to a 32-year-old G2P1 woman, due to an antenatal diagnosis of non-immune hydrops fetalis and a premature onset of labor. During pregnancy, the second-trimester sonogram revealed ...
|
|

Viral Myositis |
Viral Myositis (Portugal)
Clinical Area:
Infectious diseases
Viral myositis is a rare muscle disease that accompanies acute viral infections, mostly observed in school-age children (Maciel, Andrade, Castro, Macedo, 2022). According to these authors, it has an estimated incidence of 2.6 cases per 100,000 children during the flu season. It is mainly reported du ...
|
|
Anatomy - Human kidney and urinary system |
Sepsis in a diabetic patient with urinary tract infection (Lithuania)
Clinical Area:
Infectious diseases
A 68-year-old female patient is admitted to the emergency department with complaints of high fever, chills, generalized weakness, confusion, and dysuria that has worsened over the past 48 hours. Her daughter, who accompanied her, reports that the patient has also been experiencing lower abdominal pa ...
|
|

Lymphoblastic Leukemia |
Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL) (Portugal)
Clinical Area:
Internal medicine
Acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) is the most common type of cancer in children, accounting for approximately 25% of all pediatric cancers. It primarily affects children between 2 and 5 years of age, although it can occur at any age (Children Cancer Cause, 2021). The pathophysiology of the disease ...
|
|

Magnetic Resonance Imaging in (Near-)Term Infants with Hypoxic-Ischemic Encephalopathy |
Neonatal Hypoxic-Ischemic Encephalopathy (Portugal)
Clinical Area:
Neurology
Neonatal Hypoxic-Ischemic Encephalopathy (HIE) is a clinical syndrome of neurological dysfunction that manifests in the neonatal period. Symptoms are variable, but the most common presentations include neonatal seizures and depressed neurological status. With a multifactorial etiology, HIE is associ ...
|
|

Transfontanellar Ultrasound |
Peri-intraventricular hemorrhage in premature neonates (Portugal)
Clinical Area:
Neurology
Peri-intraventricular hemorrhage (PIVH) is a common condition in premature neonates, characterized by bleeding in the areas surrounding the cerebral ventricles, which may extend into the ventricles (intraventricular hemorrhage). This condition can result in permanent neurological damage, such as cer ...
|
|

Fetal MRI for monitoring |
Neuroblastoma (Portugal)
Clinical Area:
Neurology
Neuroblastoma is the most common malignant tumor in the neonatal period, typically originating from the adrenal medulla or sympathetic nervous system. Advances in obstetric imaging, particularly ultrasound and fetal MRI, have enabled the earlier detection of asymptomatic adrenal masses during pregna ...
|
|

What are oesophageal atresia and tracheo-oesophageal fistula? |
Oesophageal atresia (Portugal)
Clinical Area:
Pulmonology
A condition characterized by incomplete formation of the esophagus, often associated with a tracheoesophageal fistula.
The importance of early diagnosis and intervention, esophageal atresia is often associated with other congenital malformations, forming the VACTERL complex (Vertebral, Anorectal, C ...
|
|

3d image esophageal atresia |
Neonatal respiratory – esophageal atresia (Greece)
Clinical Area:
Pulmonology
A male term neonate was born at 42 weeks of gestational age, with a birth weight of 3590 g, to a 32-year-old G2P1 woman.
The mother had normal prenatal care during pregnancy and an unremarkable past medical history. She received no medications. Prenatal ultrasound in the last trimester of pregnanc ...
|
|

Stage 2: the spots become blisters |
chickenpox (Portugal)
Clinical Area:
Infectious diseases
Chickenpox is an exanthematic disease very frequent in the pediatric population and usually has a
benign course in childhood. It can prevent with vaccination. However, when it coincides with a phase of greater immunological immaturity, in
newborns up to three months of age, it may raise doubts abo ...
|
|

Asthma infographic |
ASTHMA (Portugal)
Clinical Area:
Pulmonology
Pediatric asthma is a chronic inflammatory disease of the lower airways, characterized by recurrent episodes of reversible bronchial obstruction, bronchial hyperresponsiveness, and persistent inflammation. It is a multifactorial condition involving complex interactions between genetic, immunological ...
|
|

Nephrotic Syndrome |
Nephrotic syndrome (Portugal)
Clinical Area:
Internal medicine
Nephrotic syndrome in children, especially at the age of 4, is generally caused by minimal lesions (MLD), which is the most common aetiology in this age group. The pathophysiology involves alterations in the permeability of the glomerular membrane, leading to excessive protein loss in the urine (pro ...
|
|

About Infectious Mononucleosis (Mono) |
Infectious mononucleosis, caused by the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) (Portugal)
Clinical Area:
Infectious diseases
Infectious Mononucleosis: Overview
Infectious mononucleosis is a contagious disease most commonly caused by Epstein-Barr virus (EBV). Other viruses can also cause this disease.
Symptoms range in severity for each person diagnosed with Epstein-Barr virus. Symptoms include:
Sore throat and throat ...
|
|

Congenital cytomegalovirus infection |
cytamegalovirus infection (Portugal)
Clinical Area:
Infectious diseases
Cytomegalovirus (CMV) is a wide-spread virus, with manifestations ranging from asymptomatic to severe end-organ dysfunction in immunocompromised patients with congenital CMV disease.
Most congenital CMV infections are not apparent at birth. Around 5 to 25 per cent of infants develop psychomotor, he ...
|
|

Pulmonary tuberculosis |
Tuberculosis diagnosis in an immigrant patient with persistent cough (Lithuania)
Clinical Area:
Infectious diseases
A 34-year-old male patient presents to a community health clinic with a history of a persistent productive cough lasting more than four weeks, unintentional weight loss (~6 kg over the past month), intermittent low-grade fever, and night sweats. The patient reports increased fatigue, decreased appet ...
|
|

Neuropathology specimen, Purulent meningitis, HE Stain, Hematoxylin and Eosin stain (image by Jens Florian, CC by 4.0) |
Managing a suspected case of meningococcal meningitis in the emergency room (Lithuania)
Clinical Area:
Infectious diseases
A 19-year-old previously healthy university student is brought to the emergency department by her roommates due to sudden onset of high fever (up to 40.0°C), severe headache, photophobia, neck stiffness, vomiting, and confusion over the past 12 hours. Her roommates report that she had flu-like symp ...
|
|

ST-elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) (image by ECG STAMPEDE) |
ST-elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) in a 65-year-old smoker (Lithuania)
Clinical Area:
Cardiology
A 65-year-old male with a 40-pack-year smoking history presents to the emergency department with sudden-onset retrosternal chest pain radiating to his left arm and jaw. The pain began approximately 45 minutes prior to arrival and is described as crushing and persistent, accompanied by diaphoresis, d ...
|
|

Congestive heart failure (image by Medicine Libre texts) |
Heart failure with reduced ejection fraction: diuretic management (Lithuania)
Clinical Area:
Cardiology
A 72-year-old male with a known history of ischemic cardiomyopathy presents to the emergency department with progressive shortness of breath, orthopnea, paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea, and bilateral lower extremity edema for the past 4 days. He also reports decreased exercise tolerance and weight gain ...
|
|

Atrial fibrillation with rapid ventricular response (image by Subramonian et al, 2021) |
Atrial fibrillation in a patient with hyperthyroidism: recognizing the link (Lithuania)
Clinical Area:
Cardiology
A 58-year-old woman presents to the outpatient cardiology clinic with complaints of palpitations, heat intolerance, increased sweating, weight loss (6 kg over two months), and recent episodes of shortness of breath during mild exertion. She denies chest pain, but notes occasional dizziness and fatig ...
|
|

A computed tomography (CT) scan of the head showed right-sided ischemic stroke |
Acute ischemic stroke in a patient with atrial fibrillation (Lithuania)
Clinical Area:
Neurology
A 76-year-old male with a known history of permanent atrial fibrillation (AF), hypertension, and type 2 diabetes mellitus is brought to the emergency department by ambulance after his wife noticed sudden right-sided weakness and slurred speech that began 45 minutes prior. He was last seen in his nor ...
|
|

Guillain-Barré Syndrome (image by Bae, Yuki, Kuwabara et al, 2014) |
Guillain-Barré Syndrome Following a Viral Infection (Lithuania)
Clinical Area:
Neurology
A 43-year-old male presents to the neurology department with progressive weakness and numbness in both legs, which started three days ago and has now begun to affect his arms. He reports difficulty climbing stairs and rising from a chair. The weakness is symmetrical and ascending. He also complains ...
|
|

Continuous seizure activity with high-amplitude spikes and waves typical to status epilepticus |
Status epilepticus in a known epileptic patient – emergency protocols (Lithuania)
Clinical Area:
Neurology
A 28-year-old female with a known history of epilepsy since childhood is brought to the emergency department by ambulance after experiencing continuous seizure activity for more than 10 minutes. According to her family, she had two seizures at home that were initially managed with a prescribed rescu ...
|
|

COPD exacerbation (image by Hurst, 2018) |
Acute exacerbation of COPD in a long-term smoker (Lithuania)
Clinical Area:
Pulmonology
A 71-year-old male with a 45-pack-year history of smoking and known diagnosis of GOLD stage III chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) presents to the emergency department with worsening dyspnea, increased sputum production, and purulent sputum over the past three days. He also reports increas ...
|
|

Chest X‑ray image demonstrating a pneumothorax |
Pneumothorax in a young adult with asthma (Lithuania)
Clinical Area:
Pulmonology
A 24-year-old male with a history of moderate persistent asthma presents to the emergency department with sudden-onset left-sided chest pain and shortness of breath that began 30 minutes ago while walking home. He describes the pain as sharp and pleuritic, worsened by deep inspiration, and not relie ...
|
|

Pulmonary embolism |
Pulmonary embolism in a postoperative orthopedic patient (Lithuania)
Clinical Area:
Pulmonology
A 68-year-old woman is on postoperative day 3 following a total hip replacement surgery. She has been recovering on the orthopedic ward with limited mobility and moderate pain. Suddenly, she develops acute shortness of breath, pleuritic chest pain, and lightheadedness. She becomes visibly anxious an ...
|
|

Bilateral Kidney and IVC (Moses, Fernandez, 2022) |
Acute kidney injury in a patient on NSAIDs (Lithuania)
Clinical Area:
Internal medicine
A 66-year-old female presents to the internal medicine ward with complaints of generalized weakness, decreased urine output, and mild shortness of breath over the past 48 hours. She has a history of osteoarthritis and has been taking over-the-counter nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) dai ...
|
|

Schematic representation of a simplified protocol/workflow for management of adult patients with DKA. Abbreviations: NS, normal saline, H, hour, Bl. blood, K potassium, IV intravenous (El-Remessy, 2022) |
Uncontrolled type 2 diabetes with diabetic ketoacidosis (Lithuania)
Clinical Area:
Internal medicine
A 54-year-old man with a 10-year history of type 2 diabetes mellitus is brought to the emergency department with complaints of nausea, vomiting, excessive thirst, and generalized weakness for the past 2 days. His family reports that he has been increasingly lethargic and confused over the last 6 hou ...
|
|

Serum electrolyte panel report |
Electrolyte imbalance in an adolescent with chronic vomiting (Lithuania)
Clinical Area:
Internal medicine
A 16-year-old female is admitted to the internal medicine ward from the emergency department with a history of persistent nausea and vomiting for the past 4 days. She reports feeling weak, dizzy when standing, and experiencing frequent muscle cramps. Her mother mentions that the patient has had redu ...
|
|

Hypertensive emergency |
Hypertensive emergency in a non-compliant patient (Lithuania)
Clinical Area:
Internal medicine
A 62-year-old male with a 15-year history of hypertension presents to the emergency department with severe headache, blurred vision, chest tightness, and nausea. He admits to not taking his prescribed antihypertensive medications regularly due to “feeling fine” and financial concerns. He also re ...
|
|

Gastric angiodysplasia (Lamoria, De, Sharma, 2017) |
Anemia in an elderly patient with gastrointestinal bleeding (Lithuania)
Clinical Area:
Internal medicine
An 82-year-old male is brought to the emergency department by his family due to increasing fatigue, weakness, and dizziness over the past several days. He reports black, tarry stools for the past two days but denies abdominal pain or vomiting. His past medical history includes atrial fibrillation (o ...
|
|

Polypharmacy |
Polypharmacy in a frail older adult with multiple comorbidities (Lithuania)
Clinical Area:
Internal medicine
An 85-year-old female is admitted to the internal medicine ward after a mechanical fall at home. She reports generalized fatigue, dizziness, constipation, and occasional confusion over the past week. Her medical history includes hypertension, atrial fibrillation, osteoarthritis, chronic kidney disea ...
|
|

Glucometer |
Hypoglycemia in an adolescent with type 1 diabetes on insulin therapy (Lithuania)
Clinical Area:
Internal medicine
A 15-year-old girl with a 4-year history of type 1 diabetes mellitus is brought to the emergency department by her parents after she was found pale, disoriented, and sweating profusely at home. Earlier that day, she had participated in a school sports event and skipped lunch due to feeling nauseous. ...
|
|

Doppler ultrasound image showing a hypervascular thyroid gland |
Thyroid storm in a child with undiagnosed hyperthyroidism (Lithuania)
Clinical Area:
Internal medicine
A 10-year-old girl is brought to the pediatric emergency department by her parents with high fever (39.8°C), agitation, rapid breathing, and persistent vomiting. Her parents report that she has recently lost weight despite increased appetite, has been unusually anxious and restless, and has had dif ...
|
|

Hyaline Membrane Disease |
Hyaline Membrane Disease (HMD) (Portugal)
Clinical Area:
Pulmonology
The Hyaline Membrane Disease (HMD) is one of the most severe and common causes of morbidity and mortality during the first week of life in premature newborns. The administration of corticosteroids to the pregnant woman (in cases of threatened preterm labor) accelerates fetal lung maturity and preven ...
|
|

Infective Endocarditis |
Neonatal Infective Endocarditis (Portugal)
Clinical Area:
Cardiology
Context:
Neonatal infective endocarditis is a rare but serious infection that affects the heart of newborns. It occurs when bacteria or other microorganisms infect the heart valves or the inner lining of the heart, known as the endocardium. This condition can be fatal if not diagnosed and treated p ...
|
|

Rheumatic Heart Disease: Symptoms & Causes | Pantai Hospital |
Heart disease secondary to rheumatic fever (Portugal)
Clinical Area:
Cardiology
Heart disease secondary to rheumatic fever is a condition where the heart valves have been permanently damaged by rheumatic fever. The heart valve damage may start shortly after untreated or undertreated streptococcal infection, such as strep throat or scarlet fever.
Clinical Case
Name: Female, ...
|
|

HLHS |
Hypoplastic Left Heart Syndrome (Portugal)
Clinical Area:
Cardiology
CONTEXT:
Hypoplastic Left Heart Syndrome (HLHS) is characterized by aortic atresia associated with hypoplasia of the left ventricle (LV) and the ascending aorta. It is also marked by significant hypoplasia or atresia of the mitral valve, which is present in nearly all cases. Although HLHS is a r ...
|
|

Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus (T1DM) |
Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus (T1DM) (Portugal)
Clinical Area:
Internal medicine
Diabetes Mellitus (DM) refers to a group of chronic metabolic disorders characterized by the body’s inability to regulate blood glucose levels, resulting in persistent hyperglycemia.
Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus (T1DM) is more common in children and accounts for approximately two-thirds of new diabet ...
|
|


















































































